Singing the praises of America’s favorite sandwich.
By Caleb MacLean
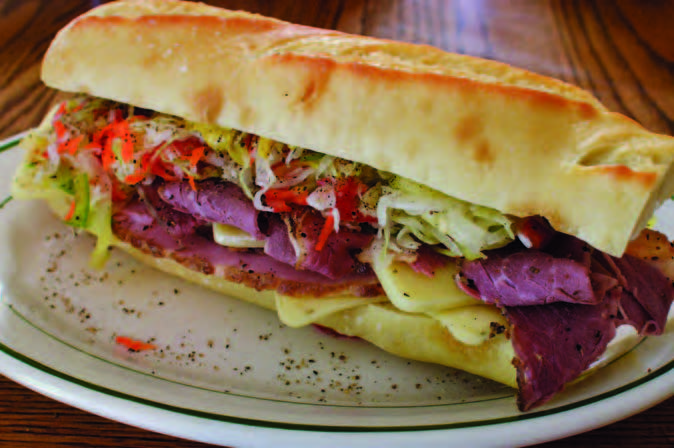
The combination of inexpensive meat and cheese, topped with greens and oil and vinegar, wrapped in a long, crusty roll dates back to the 1800s in Italy, where it was a traditional sandwich. As Italian-Americans opened grocery stores and sandwich stands in northeastern cities in the early 1900s, their signature creation grew in popularity and complexity.
Who “invented” the hero? The city of Portland, Maine claims this honor, insisting that the very first one was served up by Giovanni Amato, who ran a restaurant that’s still in business more than a century later. The more likely story is that versions of this sandwich existed throughout New England in the early part of the 20th century. During World War I, a sandwich shop in Boston was selling hero sandwiches by the hundreds to sailors at a nearby naval installation. This is where the nickname “sub” supposedly originated.

United States Navy
But wait. Our very own city of Paterson says that’s wrong. No evidence of the actual term found its way into print until the 1920s, when a group of enterprising boys managed to raise the hull of a sunken submarine from the Passaic River and donated it to the Paterson Museum. After visiting the museum, Dominic Conti, who sold hero sandwiches from his grocery store on Mill Street, rechristened his lunchtime offering the submarine sandwich. New Jersey has another important connection to the sub: the first Blimpie store opened in Hoboken in the 1960s.

Upper Case Editorial
Still another origin story for the sub involves Benedetto Capaldo, a shop-keeper in New London, who sold tasty “grinders” to his Connecticut customers. When the nearby naval base began constructing submarines in the late-1930s, daily sandwich deliveries numbered in the hundreds. Naturally, they became known as submarine sandwiches, too.

Library of Congress
The term “grinder” has a dockyard history, as well. In New England, the Italian-American workers who sanded rusty hulls were called “grinders.” Their go-to sandwich took on the same name—although some claim that the sandwich got its nickname because of how difficult it was to chew through. Until recently, there actually was an acknowledged difference between subs and grinders: subs were always cold and grinders were usually hot. So back in the day, a meatball sub would have been a meatball grinder.

Photo by David Reber

Library of Congress
What bout the hoagie? Italian-American workers at Philadelphia’s Hog Island shipyard supposedly shortened “Hog Island” to “hoagie.” But Hog Island closed down long before the nickname came into common use, so the story everyone in Philly knows is just that: a story. A better explanation is that the name started in a sandwich joint run by Al de Palma, a former jazz musician. He opened a sub shop in the City of Brotherly Love during the Depression and called his extra-large sandwiches “hoggies” (big enough to feed a hog). He eventually opened several stores around the city and, thanks to that Philly accent, hoggie became hoagie.

Photo by Jeffrey W.
As for the name “hero,” it became popular in the New York/New Jersey area in the late 1930s. The theory that it is derived from the Greek gyro sandwich doesn’t quite work—gyros didn’t become popular in New York until the 1960s. In 1936, a food columnist for the New York Herald Tribune described an Italian sandwich so huge you had to be a “hero to eat it.” The paper had a circulation of 300,000 at the time, so thousands of readers began calling the sandwich by its new name. Cops, bank guards and armored car crews popularized the term by the end of the decade.
Did You Know?
During the many decades when the hero sandwich was a staple of the working man’s lunchbox, one of its key construction details was the placement of the cheese. The first and last layer was almost always made of cheese slices. They prevented oil, vinegar and other condiments from migrating into the bread.
Did You Know?
Other names for the iconic sandwich include torpedo, wedge, Dagwood, zep and bomber. In New Orleans the “poor boy” (pronounced po’boy) resembles the traditional sub, but was originally constructed to mimic the courses of a meal.